Get to know Solar Energy
975 Views |

Solar energy is very significant nowadays as it is clean energy, environmentally-friendly and never ends causing many of you to turn attention to the generation of electricity from solar system, whether it is a home, office building, factory, or even solar farm. But many of you still wonder what solar cell is and how it works. Let’s go for the answers.
A solar, or photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
A solar cell is made of two types of semiconductors, called p-type and n-type silicon. The p-type silicon is produced by adding atoms—such as boron or gallium—that have one less electron in their outer energy level than does silicon. Because boron has one less electron than is required to form the bonds with the surrounding silicon atoms, an electron vacancy or “hole” is created.
The n-type silicon is made by including atoms that have one more electron in their outer level than does silicon, such as phosphorus. Phosphorus has five electrons in its outer energy level, not four. It bonds with its silicon neighbor atoms, but one electron is not involved in bonding. Instead, it is free to move inside the silicon structure.
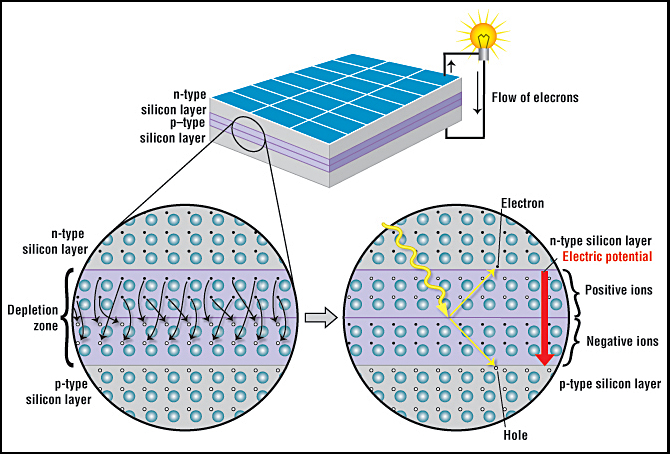
Cr. Anthony Fernandez, American Chemical Society
Solar Technologies
There are three main ways to use solar energy: photovoltaics, systems Integration, and concentrating solar power.
The process of photovoltaics is simple. When the sun shines onto a solar panel, energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the PV cells in the panel and can be used to power anything from small electronics up to homes and large commercial businesses.

Concentrating solar power (CSP) applications uses the heat generated by the sun to provide space. It uses mirrors to reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect solar energy and convert it to heat, which can then be used to produce electricity or stored for later use. It is used primarily in very large power plants.
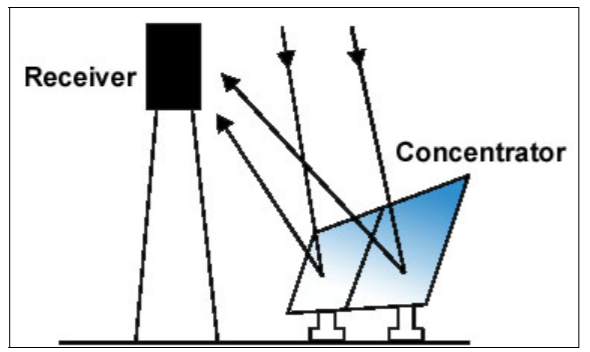
Cr.Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency


