Components and Types of Solar Panels
1866 Views |

Nowadays, it is undeniable that solar energy is a more popular alternative energy than before as the efficiency of solar panels has been improved to generate more electricity and high quality of the panels.As a result, the price of solar panels is greatly reduced.
How efficient and affordable solar cells can be. Answering that question means understanding how solar energy work, how solar panels are manufactured and what the parts of a solar panel are. In this article, we’ll explain what parts are required to manufacture a solar panel and types of it.
What are solar panels made of?
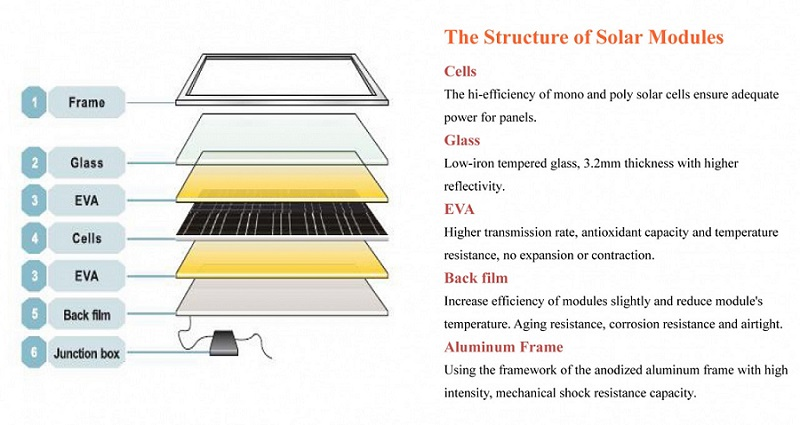
The materials used to make cells are mainly silicon and semiconductors. The main components consist of anode and cathode that generate an electric field and combine with solar energy to produce electricity. The materials used to manufacture the cells for solar panels are only one part of the solar panel itself. The solar panel manufacturing process usually brings together six different components. Here are the common parts of a solar panel:
- Silicon solar cells
- Metal frame
- Glass sheet for casing
- EVA (EthyleneVinyl Acetate )
- Backsheet
- Junction box
Source: Eco sources
Types of solar panels
1. Monocrystalline or Singlecrystalline solar panels are made of high purity silicon, then stir it until the crystals stick together at the core forming a cylindrical rod. After that, the process includes cutting individual wafers of silicon that can be affixed onto a solar panel to achieve maximum efficiency. The shape of cell looks like a square called wafer with a dark color. Monocrystalline silicon cells are more efficient than polycrystalline or amorphous solar. Producing individual monocrystalline wafers is more labor-intensive, and consequently, they are also more expensive to manufacture than poly crystalline cells.



For anyone wanting to install solar who is considering a do-it-yourself route, there are a number of factors to consider such as warranties, the longevity of output, efficiency and overall cost. If you’re interested in solar installation from highly-skilled engineer with high quality solar panels, please contact our staff for the quotation and consultation for free.
Ref. Energysage


